Shop Configuration
A crucial part of every Shop is the configuration. It allows you to change settings like language, currency, image sizes, authentication, payment gateways. You can also customize the checkout validation logic, order numbering, reviews.
The config is also to be used to enable or disable features like multi-channel, reviews, advanced pricing or tax calculation.
It consists of one or more files in the repository'sconfig/ folder.
The list of possible config files in the config directory:
vanilo.json: configures the ecommerce featuresshop.json: basic application configurationmail.json: e-mail sending configurationchannels.json: multi-channel-specific configurationstorefronts.json: configuration for multi-storefront environmentsbff.yml: Storefront API documentation customization
Environment Variables
The JSON configuration files may contain credentials that you may not want to add to the version control. Additionally, you may want to use different configuration values for different environments (production, staging, dev).
To enable this, the configuration values can use environment values using the ${{ env.VARIABLE_NAME }} format:
{
"driver": "${{ env.MAIL_DRIVER }}"
}
Variables like MAIL_DRIVER can be set in the Admin Panel → DEV ZONE → Environment menu.
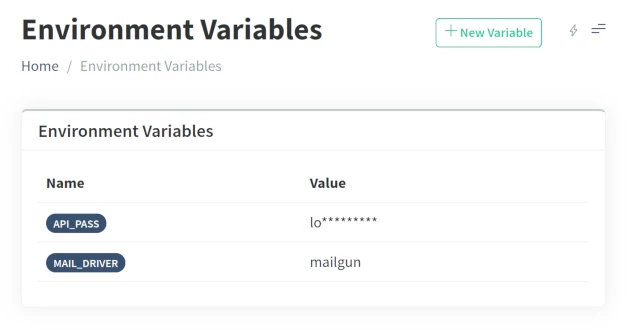
The value of the given configuration will be substituted with the variable's value.
Currency
To configure the base currency of your shop, you need to define the following options in the config/vanilo.json file:
{
"foundation": {
"currency": {
"code": "EUR",
"format": "%1$g %2$s",
"sign": "€"
}
}
}
where the code field's value must be the 3 letter ISO-4217 currency code
of the base currency the shop is using.
The sign field will be used to display the prices in the given currency, for example $ (dollar), € (euro),
¥ (yen) or Fr (franc).
The format is an sprintf compatible format string that
takes the amount as the first and the currency sign as the second parameter.
The format_price() helper function will use it.
// format: "%1$g %2$s", sign: '€'
format_price(140)
// => "140 €"
// format: "%2$s%1$g", sign: '$'
format_price(140)
// => "$140"
Data Injection
The templates receive their own respective data (products, cart, etc).
Additionally, you can also define custom data to inject into the home page and
info pages in the config/vanilo.json file:
{
"cloud": {
"info": {
"kawasaki-summer-sale-2024": {
"inject": {
"featured": "product.bySkus(ER650MPFNN,EJ800EPFNN,ZR900NPFNN)",
"kawasaki": "taxon.bySlug(kawasaki)"
}
}
}
}
}
Refer to the Hick Script page to learn the available syntax for injection.
The example above will take the 4 latest products and the taxonomy "brands" and inject them into the blade/twig file
as $featured and $kawasaki variables, when rendering the page on the /info/kawasaki-summer-sale-2024 route.
- The
$featuredvariable will be a collection with 3 products having the SKUs ER650MPFNN,EJ800EPFNN and ZR900NPFNN. - The
$kawasakivariable will be a Taxon (Category) object that has the "kawasaki" slug
For injecting data in a multi-storefront setup, see to the Multi Storefront Documentation
Global Data Injection
You can inject data into every page globally. Global data will be available in every template of your Storefront.
To do this, add entries in the config/vanilo.json file under the cloud.view.share key:
{
"cloud": {
"view": {
"share": [
{
"name": "categories",
"value": "taxonomy.bySlug(category)"
}
]
}
}
}
The example above will load the entire "category" taxonomy object and inject it as $categories variable into every
blade/twig file of your shop. This can be useful when the variable is needed by the shop layout.
Refer to the Hick Script page to learn the available syntax for injection.
To configure the email sending for your shop, you need to define the options in the config/mail.json file.
The supported E-mail drivers are: smtp, mailcoach, mailgun, postmark, ses
SMTP
{
"driver": "smtp",
"host": "email-smtp.eu-central-1.amazonaws.com",
"port": 587,
"username": "XXXXXXXXXXX",
"password": "XXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX",
"encryption": "tls",
"from": {
"address": "[email protected]",
"name": "Shop Name"
}
}
Mailcoach
{
"driver": "mailcoach",
"domain": "test.mailcoach.app",
"token": "XXXXXXXXXX",
"from": {
"address": "[email protected]",
"name": "Shop Name"
}
}
Mailgun
{
"driver": "mailgun",
"mailgun": {
"domain" : "MAILGUN_DOMAIN",
"secret" : "MAILGUN_SECRET",
"endpoint" : "api.mailgun.net"
},
"from": {
"address": "[email protected]",
"name": "Shop Name"
}
}
Postmark
{
"driver": "postmark",
"postmark": {
"token": "POSTMARK_TOKEN"
},
"from": {
"address": "[email protected]",
"name": "Shop Name"
}
}
Amazon SES
{
"driver": "ses",
"ses": {
"key": "ACCESS_KEY",
"secret": "SECRET",
"region": "eu-central-1"
},
"from": {
"address": "[email protected]",
"name": "Shop Name"
}
}
Image Sizes
Images uploaded in Admin or via the REST API are resized to various sizes. These are called "variants" and you can freely define the names, sizes and the cropping method of these variants as per your needs.
See the Images Page for detailed information about image handling in Vanilo Cloud
The image sizes need to be defined in the config/vanilo.json file:
{
"foundation": {
"image": {
"variants": {
"thumbnail": {
"width": 250,
"height": 250,
"fit": "crop"
},
"medium": {
"width": 500,
"height": 360,
"fit": "crop"
}
}
}
}
}
These settings will apply to images of products, taxonomies and taxons.
If you need different variants for any of products/taxonomies/taxons, you can define specific variant for them, that
will override the image sizes defined under the foundation.image.variants configuration.
The image configuration can be placed under the following JSON keys:
foundation.image.variants: applies to the images of all entities (product, taxon, taxonomy).foundation.image.product.variants: applies to product images only, overrides the common image configurationfoundation.image.taxon.variants: applies to taxon images only, overrides the common image configurationfoundation.image.taxonomy.variants: applies to taxonomy images only, overrides the common image configuration
The example below will create a single variant called "banner" for images uploaded to taxons and taxonomies, and two variants called "index" and "preview" for images uploaded to products:
{
"foundation": {
"image": {
"variants": {
"banner": {
"width": 1280,
"height": 360,
"fit": "crop"
}
},
"product": {
"index": {
"width": 360,
"height": 360,
"fit": "crop"
},
"preview": {
"width": 720,
"height": 720,
"fit": "crop"
}
}
}
}
}
Fit Methods
The "fit" keys can take the following values:
| Method | What it does |
|---|---|
contain |
Resizes the image to fit within the width and height boundaries without cropping, distorting or altering the aspect ratio. |
crop |
Resizes the image to fill the width and height boundaries and crops any excess image data. The resulting image will match the width and height constraints without distorting the image. |
fill |
Resizes the image to fit within the width and height boundaries without cropping or distorting the image, and the remaining space is filled with the background color. The resulting image will match the constraining dimensions. |
stretch |
Stretches the image to fit the constraining dimensions exactly. The resulting image will fill the dimensions, and will not maintain the aspect ratio of the input image. |
max |
Resizes the image to fit within the width and height boundaries without cropping, distorting or altering the aspect ratio, and will also not increase the size of the image if it is smaller than the output size. |
Order
The order configuration allows you to define how the order numbers are generated.
Vanilo Cloud has 3 number generators: sequential_number, nano_id and time_hash (default).
To set the order number generator, set the order.number.generator key in the vanilo.json file:
{
"order": {
"number": {
"generator": "nano_id"
}
}
}
Each generator has further settings, that are described below.
Sequential Number
Generates a sequential order number like 5684975 or ORD-0078. Further settings allow you to set the starting number, a prefix, and padding:
{
"order": {
"number": {
"generator": "sequential_number",
"sequential_number": {
"start_sequence_from": 100,
"prefix": "ORD-",
"pad_length": 4,
"pad_string": 0
}
}
}
}
The example above will generate order numbers: ORD-0100, ORD-0101, ORD-0102 and so on.
Time Hash
This is the default order number generator
Uses the current date and time down to milliseconds and some randomness to generate a unique sequence of letters like "6P3-0EB3-79G8".
{
"order": {
"number": {
"generator": "time_hash",
"time_hash": {
"start_base_date": "2024-01-01",
"uppercase": true,
"high_variance": false
}
}
}
}
The start_base_date setting influences where the number generation starts from.
If the high_variance is enabled then the generated number will be longer like "6TF-0QFC-30U2-71FN". This setting
should be enabled if you expect processing at least 20 order per second.
Nano ID
Generates a Nano ID like "7YV9PC7QEZE6" for the order number.
By default, the nano id generator creates a 12 character long id, using only digits 0-9 and uppercase characters A-Z. You can change the size and the characters used in the ID. It's not recommended to use shorter than 8-10 character long order numbers to avoid possible duplicates.
{
"order": {
"number": {
"generator": "nano_id",
"nano_id": {
"size": "10",
"alphabet": "123456789ABCDEFGHIJKLMNPQRSTUVWXYZ"
}
}
}
}
The example above will generate 10 character long nano ids, and won't use 0 and O characters in the generated numbers.
Checkout
- shipping_countries
- billing_countries
- validation rules
Payment
The payment gateways have to be configured in the vanilo.json file, under the payment key. Each gateway has its
own unique configuration values.
It is recommended to store the credentials in Environment Variables and not directly in the config files.
Mollie
{
"payment": {
"mollie": {
"api_key": "live_xyz1234"
}
}
}
Stripe
{
"payment": {
"stripe": {
"public_key": "pk_test_12abcd",
"secret_key": "sk_test_12xyz0",
"create_customer": false
}
}
}
If the create_customer configuration is true, then a Stripe customer lookup/creation will be attempted based on the
shopper's email address upon every payment intent. This is encouraged by Stripe, but not mandatory, and is disabled by
default.
Netopia
{
"payment": {
"netopia": {
"signature": "1234-XXXX-YYYY-ZZZZ-AAAA",
"public_certificate_path": "netopia/live.1234-XXXX-YYYY-ZZZZ-AAAA.public.cer",
"private_certificate_path": "netopia/live.1234-XXXX-YYYY-ZZZZ-AAAAprivate.key",
"sandbox": false
}
}
}
Authentication
Shoppers can register on your site, if the auth/login and auth/register views are present.
E-mail verification
By default, the registration works without email verification. If you want to enforce users to validate their
email address set the cloud.auth.must_verify_email configuration to true:
vanilo.json:
{
"cloud": {
"auth": {
"must_verify_email": true
}
}
}
Captcha
It is possible to protect the login and register routes with captcha. If it's enabled, the user will have to solve the captcha in order to complete the action. Currently, the Cloudflare Turnstile method is supported.
vanilo.json:
{
"cloud": {
"auth": {
"captcha": {
"type": "cloudflare",
"on_pages": ["login", "register"],
"cloudflare": {
"site_key": "",
"secret_key": ""
}
}
}
}
}
If you set the cloud.auth.captcha.type to cloudflare, then the feature will be enabled.
In this case, you'll also need to populate the site_key and secret_key values.
The cloud.auth.captcha.on_pages array accepts the "login" and "register" values. It defines
which pages are protected by the captcha. You can enable the captcha only on one, or on both pages.
The captcha snippet is not auto-injected on your login/register page. If you want to use it, you have
to add the snippet manually, or you can simply use the cloudflare_turnstile() helper function:
Blade Example:
<form action="{{ route('shop.register.submit') }}" method="POST">
@csrf
[...fields...]
{!! cloudflare_turnstile() !!}
<button type="submit">{{ __('Register') }}</button>
</form>
Twig Example:
<form action="{{ route('shop.register.submit') }}" method="POST">
{{ csrf_field()|raw }}
[...fields...]
{{ cloudflare_turnstile()|raw }}
<button type="submit">{{ __('Register') }}</button>
</form>
Redirect URLs
vanilo.json:
{
"cloud": {
"urls": {
"after_login": "/u/account",
"after_registration": "/u/account",
"after_logout": "/",
"after_verification": "/"
}
}
}
Tax Configuration
vanilo.json
{
"taxes": {
"engine": {
"driver": "none(default)|simple|eu|canada"
}
}
}
Features
To enable extra, non-default features in your shop, set the features.<feature_name>.is_enabled config value to true:
{
"features": {
"multi_channel": {
"is_enabled": true
},
"pricing": {
"is_enabled": true
},
"search_engine": {
"is_enabled": true
},
"inventory": {
"is_enabled": true
}
}
}
These are the Vanilo Cloud features which are turned off by default:
For further usage and configuration details refer to each feature's documentation page.
Reviews
The built-in review system can be enabled and configured:
{
"cloud": {
"reviews": {
"enabled": true,
"num_stars": 5,
"on_product_page": 2
}
}
}
The num_stars defines what the best rating is, typically 5.
The on_product_page defines the number of reviews to inject into the product page.
StoreFront Api
The configuration of the StoreFront API is in the vanilo.json file under the cloud.bff key.
BFF stands for "Backend for Frontend", the initial name of the Vanilo Cloud StoreFront API.
Access Control
By default, the StoreFront API is publicly accessible, the same way as other StoreFront endpoints that return HTML responses. It also applies to the Swagger spec + API documentation.
To disable public access to these features set the deny_public_access and allow_swagger_public_access
values to false, respectively:
{
"cloud": {
"bff": {
"deny_public_access": false,
"allow_swagger_public_access": true
}
}
}
If the public access is disabled, it can only be accessed with the API key of a Customer user:
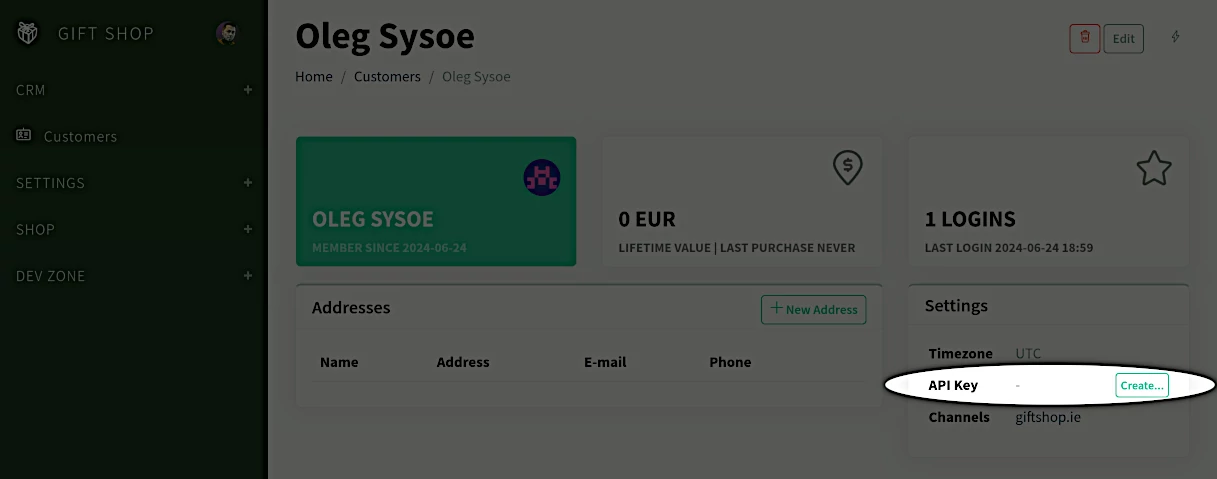
The API key needs to be passed as the X-Api-Key header in every request made to the StoreFront API.
Custom Endpoints
It is possible to extend the StoreFront API with custom endpoints.
This will allow to use the API including authentication, and integrate external code with the StoreFront API.
The example below will add the POST endpoint at yourshop.com/bff/myendpoint,
and proxy the request to the https://remote-url.workers.dev/remote-path URL.
The X-Access-Key and Any-Other-HTTP-Header will be added to the forwarded request.
The response from the remote URL will be passed back to the caller.
{
"cloud": {
"bff": {
"extensions": {
"myendpoint": {
"POST": {
"handler": {
"url": "https://remote-url.workers.dev/remote-path",
"headers": {
"X-Access-Key": "$",
"Any-Other-HTTP-Header": "Any Value"
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
Misc
If you use master products & variants the cloud.concat_master_and_variant_title configuration can be used to
display variant titles as the master title + variant title. This affects the output of the product_title() helper,
and the way the product name gets stored with the order items.
Let's say you have a master product with name "Puma Suede Classic" and two variants:
- "Puma Suede Classic Green", and
- "Puma Suede Classic Blue".
By default, the concat_master_and_variant_title configuration is FALSE, meaning, the variant's title will
be like "Puma Suede Classic Green".
But you can name the master/variants differently. Let's say the master product has the name "Puma Suede Classic" and it has 3 variants with names: "Green", "Blue".
If you set concat_master_and_variant_title to true, then the variants will be displayed as
"Puma Suede Classic Green", etc.
Both variants are valid, and it's up to you how you want to structure the naming of variants.